5 Tips to Heal Eczema Naturally
Eczema is a skin condition that more than 30 million suffer from in the United States. The exact cause of the condition is unknown, although some medical professionals believe there is a link between eczema and the body reacting to an irritant, such as food. Eczema is not contagious, but you are more likely to have it if someone else in your family has it. You can limit eczema outbreaks as well with these natural tips:
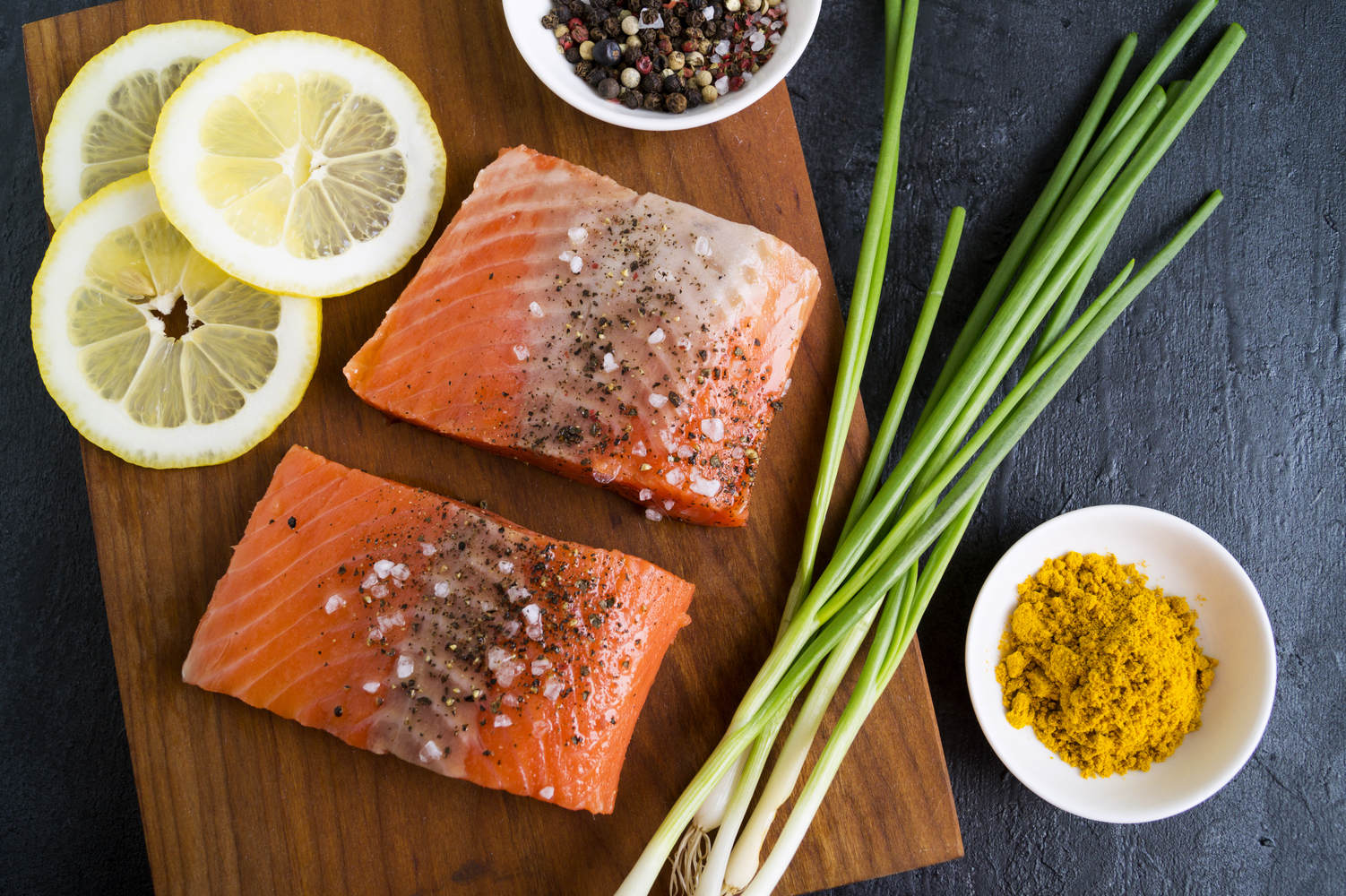
1. Foods to eat
To help ease eczema look for foods that contain anti-inflammatory benefits. Examples of these include fishes that are high in omega-3 fatty acids such as tuna, salmon, mackerel, sardines, and herring. Probiotics also help with eczema and can be found in yogurt, miso soup, and tempeh. Finally, look for foods high in inflammation fighting factors such as apples, broccoli, cherries, spinach, and kale.
2. Foods to avoid
If you have eczema you will find certain foods will cause flare ups. Although food reactions vary by person, typically people with eczema should avoid citrus fruits such as grapefruit and oranges, dairy, eggs, soy, gluten, wheat, some spices including cloves and cinnamon, vanilla, tomatoes, and certain nuts.
3. Minimize itching and scratching
Itching your eczema provides short term relief, but can make the condition worse. Constant itchy can lead to sores becoming inflamed or bleeding. Instead of itching try applying a cool, wet compress to the itchy area. Oatmeal baths also provide soothing relief.
4. Use natural topicals like aloe vera
Try using natural topicals such as aloe vera to add moisture to the skin. This can help reduce the inflamed areas of the skin.
5. Avoid abrasive clothing
Try to avoid synthetic fabrics that often irritate the eczema including wool, nylon, and polyester. Instead opt for clothing that allows your skin to breathe like cotton, silk and bamboo.
Eczema exists in many different types, such as:
- Atopic dermatitis: Atopic dermatitis is the most common form of eczema. Symptoms of eczema or atopic dermatitis can range and often start in childhood. Symptoms include dry skin patches, itchy skin, hot skin patches, peeling or cracked skin, oozing of patches, and areas of swelling.
- Contact dermatitis: There are two forms of contact dermatitis. Irritant contact dermatitis occurs when a person’s skin meets irritates including fabric softeners, acid and alkalis, detergents, hair dyes, some shampoos, and weed killers. Allergic contact dermatitis occurs when a person comes in contact with allergens such as latex or rubber, glue, adhesives, some clothing and fabrics, plants such as poison ivy or sumac, metals such as nickel and cobalt, and ingredients in some makeup, nail polishes, creams, and other cosmetics.
- Dyshidrotic eczema: This type of eczema is more common among adults under the age of 40. It causes intense itching and blisters on the hands and feet.
- Discoid eczema: Discoid eczema appears as red disc shaped patches on the legs, torso, and forearms. Triggers include dry skin, an insect bite, cold weather, a bacterial infection, poor blood flow, certain medications, and sensitivity to metals and formaldehyde.
- Varicose eczema: This type of eczema is common in older adults with varicose veins issues. Symptoms occur in the lower legs and include hot itchy spots, blisters, scaly skin, cracked or crusty patches.